14+ cellular respiration measuring energy production in plants
576 The Krebs Cycle. Must contain at least 4 different symbols.

Measuring Energy Production In Plants Docx Tutorial 4 Assignment 1 Preparing An Abstract Virtual Lab 1 Cellular Respiration Measuring Energy Course Hero
Physicists often discuss ideal test results that would occur in a perfect vacuum which they sometimes simply call vacuum or free space and use the term.

. Just as in the electron transport chain of cellular respiration. Carbon dioxide CO 2 is an important trace gas in Earths atmosphereIt is an integral part of the carbon cycle a biogeochemical cycle in which carbon is exchanged between the Earths oceans soil rocks and the biosphere. Kinetic energy is determined by the movement of an object or the composite motion of the components of an object and potential energy reflects the potential of an object to have motion and generally is a function of the.
Metabolism m ə ˈ t æ b ə l ɪ z ə m from Greek. Proteins are assembled from amino acids using information encoded in genes. Fate of primary production inputs to soil.
Adenosine triphosphate ATP is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells such as muscle contraction nerve impulse propagation condensate dissolution and chemical synthesis. ASCII characters only characters found on a standard US keyboard. The genetic code is a set of three-nucleotide sets called codons and each three-nucleotide combination designates an amino acid for example AUG.
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. Finally nuclear energy is the energy stored in the nucleus of an atom. Primary production is the production of chemical energy in organic compounds by living organismsThe main source of this energy is sunlight but a minute fraction of primary production is driven by lithotrophic organisms using the chemical energy of inorganic molecules.
Ultraviolet light has too much energy for photosynthesis and infrared light does not have enough. Search read and discover. μεταβολή metabolē change is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organismsThe three main purposes of metabolism are.
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula C 6 H 12 O 6Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide a subcategory of carbohydratesGlucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide using energy from sunlight where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls the most abundant carbohydrate in the world. Light The manner in which solar energy travels is described as waves. An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity.
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that through cellular respiration can later be released to fuel the organisms activitiesSome of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules such as sugars and starches which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water hence the name. A vacuum is a space devoid of matterThe word is derived from the Latin adjective vacuus for vacant or voidAn approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Each protein has its own unique amino acid sequence that is specified by the nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding this protein.
Plant-derived organic carbon after appropriate extracellular depolymerisation is processed by soil microorganisms to CO 2 microbial biomass and extracellular substancesMicrobial necromass and metabolites are the precursors for stable soil organic matter while extracellular microbial carbon may also. Regardless of its source this energy is used to synthesize complex organic molecules from simpler. The conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes.
572 Structure of the Mitochondrion. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table a highly reactive nonmetal and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compoundsOxygen is Earths most abundant element and after hydrogen and helium it is the third-most abundant element in the. However not all light can be used for photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide chemical formula CO 2 is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. Remember that cellular respiration is the reverse process from photosynthesis as follows. 575 The Link Reaction.
577 The Role of Coenzymes. 343 Digestive System Processes. However darkness has no effect on respiration.
The air spaces in the leaf are saturated with water vapour which exits the leaf through the stomata in a process known as transpirationTherefore plants cannot gain carbon. Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 into pyruvate CH 3 COCO 2 HThe free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate ATP and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NADH. Soil is a major component of the Earths ecosystemThe worlds ecosystems are impacted in far-reaching ways by the processes carried out in the soil with effects ranging from ozone depletion and global warming to rainforest destruction and water pollutionWith respect to Earths carbon cycle soil acts as an important carbon reservoir and it is potentially one of the.
Scientists can determine the amount of energy of a wave by measuring its. This energy can be manifested in two different ways. The conversion of food to building blocks for proteins lipids nucleic acids and some carbohydrates.
Bookshelf provides free online access to books and documents in life science and healthcare. 6 to 30 characters long. First is the fission process.
573 The Four Stages in Aerobic Respiration. The ions build up energy because of diffusion and. 5710 Energy Yield of Aerobic vs Anaerobic.
When consumed in metabolic. In the air carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation acting as a greenhouse gasIt is a trace gas in Earths atmosphere at 417. CO 2 gain and water loss.
Only the visible light range blue to red is considered photosynthetically active radiation 1. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. A carbon footprint is the total greenhouse gas GHG emissions caused by an individual event organization service place or product expressed as carbon dioxide equivalent CO 2 e.
An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult. Greenhouse gases including the carbon-containing gases carbon dioxide and methane can be emitted through the burning of fossil fuels land clearance and the production and. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life in which substrate molecules are converted into products.
The total energy of a system can be subdivided and classified into potential energy kinetic energy or combinations of the two in various ways. Found in all known forms of life ATP is often referred to as the molecular unit of currency of intracellular energy transfer. Plants and other photoautotrophs use solar energy to produce carbohydrate from atmospheric carbon dioxide and water by photosynthesis.
Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymesCapture of bond energy of carbohydrates. Photosynthetic production peaks during the day and declines after dark 24. Carbon dioxide a key reactant in photosynthesis is present in the atmosphere at a concentration of about 400 ppmMost plants require the stomata to be open during daytime.
In nuclear fission an unstable nucleus. C 6 H 12 O 2 à 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O. 342 Nutrition and Energy Production.
Photosynthesis stores energy and respiration releases it for use in functions such as reproduction and basic maintenance. Please contact Savvas Learning Company for product support. 571 The Need for Cellular Respiration.

Cellular Respiration Measuring Energy Production In Plants Pdf 11 4 2020 S Lab A De A Carolyn M H Ce S He I A E A D E De E D He He He Bea A E Course Hero

Understanding Photosynthesis With Max Axiom Super Scientist Capstone Young Readers

Pdf Tumor Energy Metabolism And Potential Of 3 Bromopyruvate As An Inhibitor Of Aerobic Glycolysis Implications In Tumor Treatment

Cell Respiration Labquest Activity 11b Ppt Download

Enhanced Oxidative Phosphorylation In Nkt Cells Is Essential For Their Survival And Function Pnas
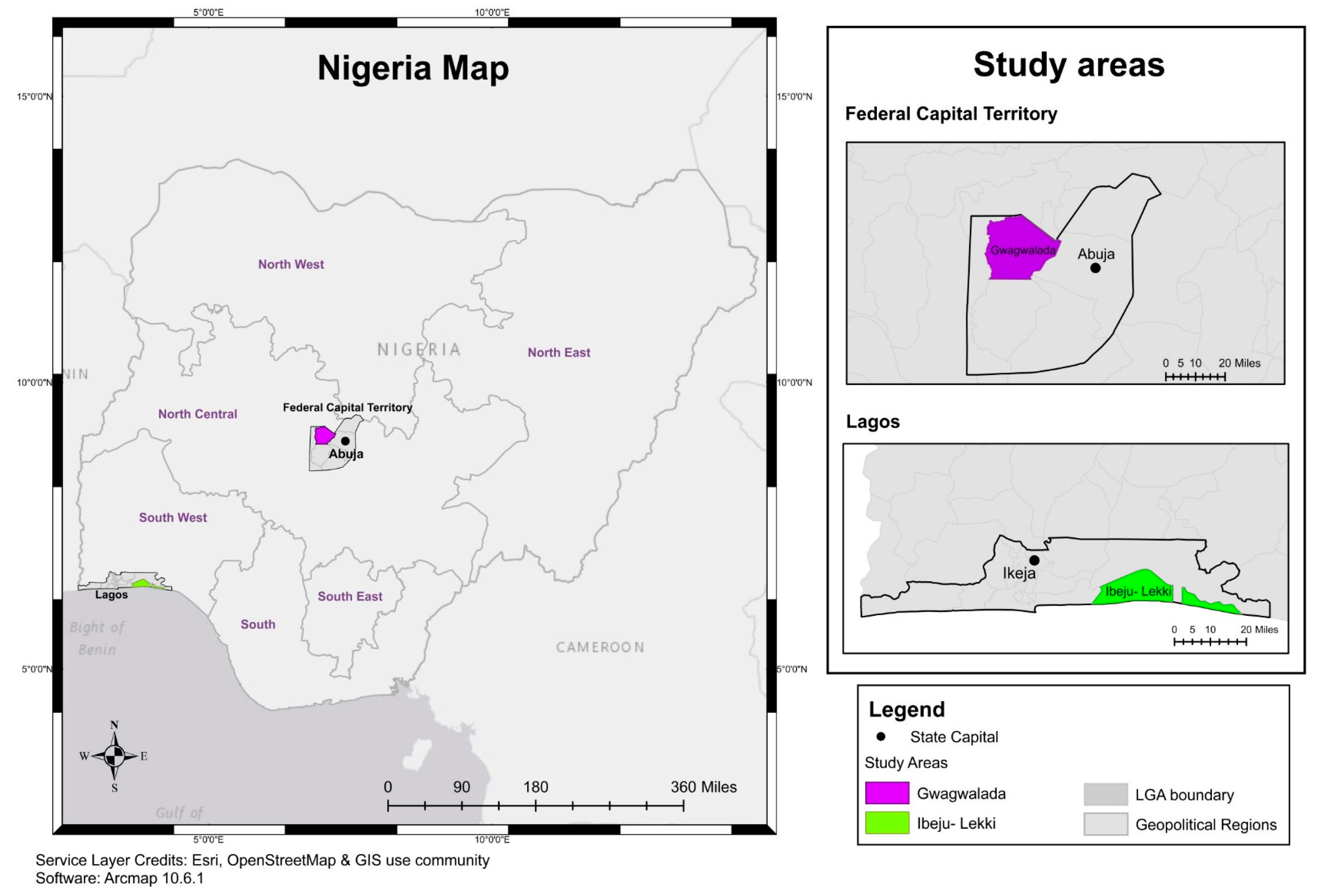
Energies Free Full Text The Energy Lock In Effect Of Solar Home Systems A Case Study In Rural Nigeria Html

Cellular Respiration Measuring Energy Production In Plants Pdf 4 10 2020 Laboratory Simulation Student Alicia My Hypothesis Cellular Respiration Course Hero

Cellular Respiration Measurind Energy Production In Chegg Com

Lab 5 Cellular Respiration Lab 5 Cellular Respiration Description Using Respirometer To Measure Rate Of O 2 Production By Pea Seeds Ppt Download

Cellular Respiration Measuring Energy Production In Plants Pdf 4 10 2020 Laboratory Simulation Student Alicia My Hypothesis Cellular Respiration Course Hero

Micronutrients In Health And Diseases

Distance Learning Yeast Cellular Respiration

Solved Exercise 16 Aerobic Respiration In Plants And Chegg Com

Cellular Respiration Data Analysis Mr Stewart S Biology Class

Amy Brown Science Measuring The Rate Of Cellular Respiration

Cellular Respiration Activity Beyond Science Resources
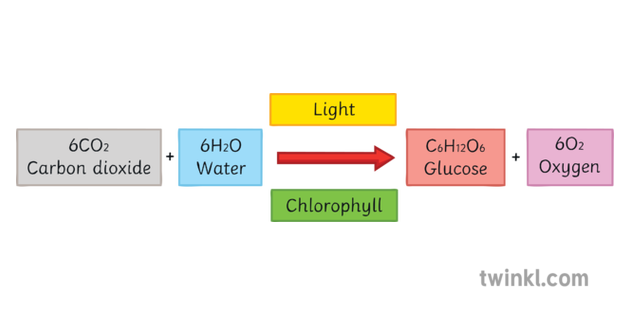
What Is Glucose Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki Twinkl